
Understanding Dog to Human Years: Accurate Aging Insights
Overview
This article delves into the complexities of converting dog years to human years, recognizing that the traditional 7:1 ratio can be misleading for concerned pet owners. It highlights a more precise formula:
Human Age = 16 * ln(Dog Age) + 31.
This formula takes into account essential factors such as breed and size, allowing you to better understand your dog’s unique aging process. By embracing this knowledge, pet owners can provide more tailored care and nutrition, addressing their beloved companions’ specific needs as they grow older.
Introduction
Understanding the aging process of dogs is more intricate than the simple notion that one dog year equals seven human years. This common misconception can lead to feelings of confusion and concern among pet owners, as it overlooks the significant variations in aging influenced by breed, size, and health.
By exploring a scientifically-backed formula that accurately converts dog years to human years, pet owners can gain valuable insights into their furry friends’ life stages and health requirements.
Recognizing these differences not only enhances our understanding but can also transform the way we care for our beloved pets, ensuring their well-being throughout their lives.
How might this deeper awareness impact the love and care we provide to our four-legged companions?
Explore the Basics of Dog Aging: Understanding the Dog Years to Human Years Conversion
It’s a common belief that one canine lifespan equals seven human years, but this oversimplifies the complex aging journey of our beloved dogs when converting dog to human years. As pet owners, it’s crucial to recognize that dogs mature at different rates based on their breed and size, which can deeply affect their health and well-being. Generally, smaller breeds enjoy longer lifespans and age more slowly compared to their larger counterparts. To truly understand our furry friends’ ages in dog to human years, we can use a more precise formula that considers their age in intervals and applies a logarithmic function, offering clearer insights into their life stage and health needs.
Researchers have developed a formula that reads:
Human Age = 16 * ln(Dog Age) + 31
This formula allows for a more accurate calculation for dogs older than one year, reflecting their biological aging process far better than the outdated 7:1 ratio. For instance, research indicates that a Labrador Retriever typically lives around 13.1 years, while smaller breeds like the Lancashire Heeler can reach up to 15.4 years. By understanding these nuances in dog aging, we can provide better care for our pets and foster a deeper appreciation for their unique health and happiness. After all, every moment spent with them is precious, and being aware of their aging process helps us cherish those moments even more.
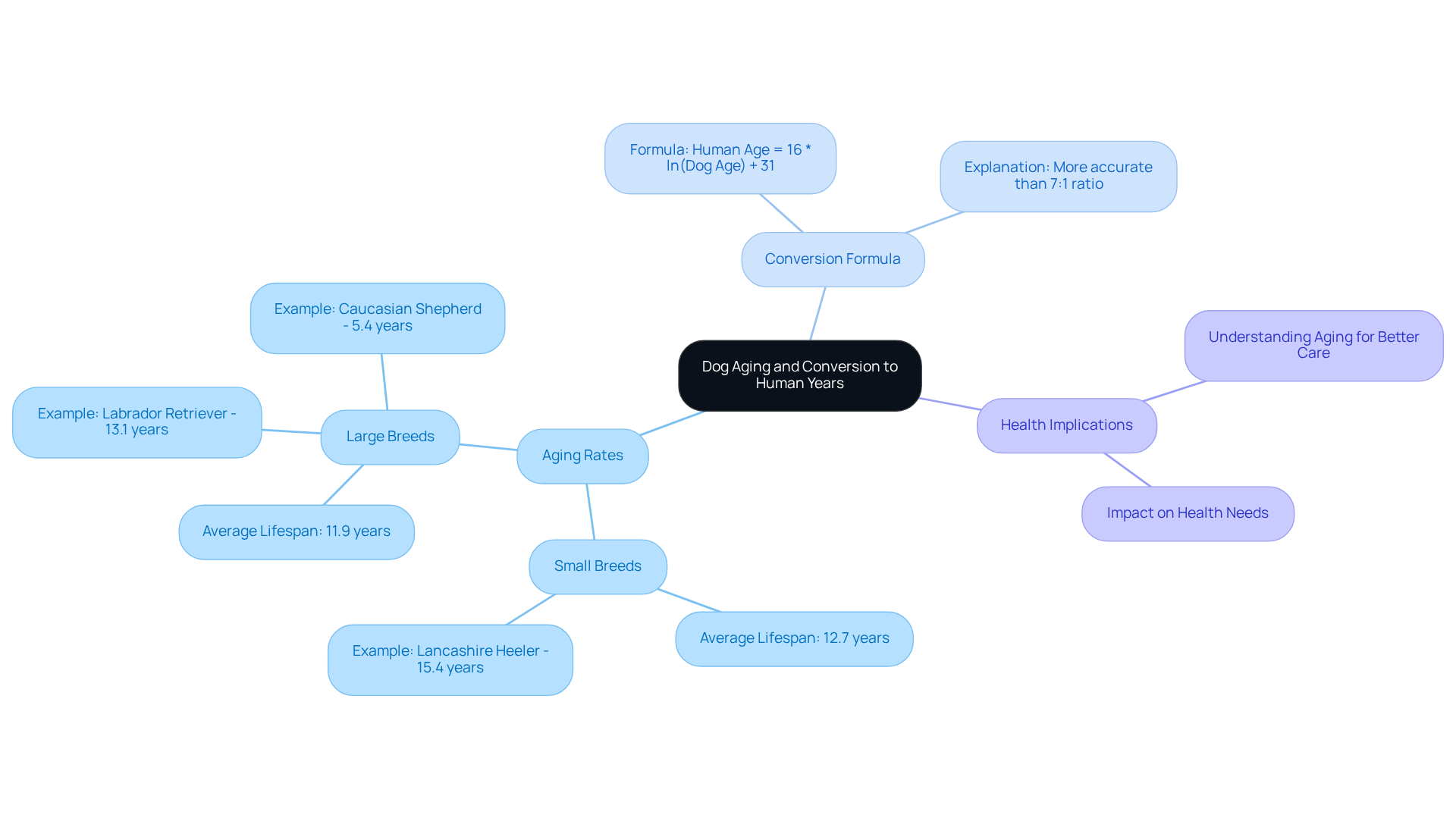
Debunk the 7:1 Myth: Factors Influencing Dog Aging Beyond Simple Ratios
The common belief that one canine year equals seven human years is a misunderstanding that fails to capture the complexities of aging when considering dog to human years. It’s essential to recognize that a dog’s aging process is influenced by various factors, including breed, size, and overall health. For example:
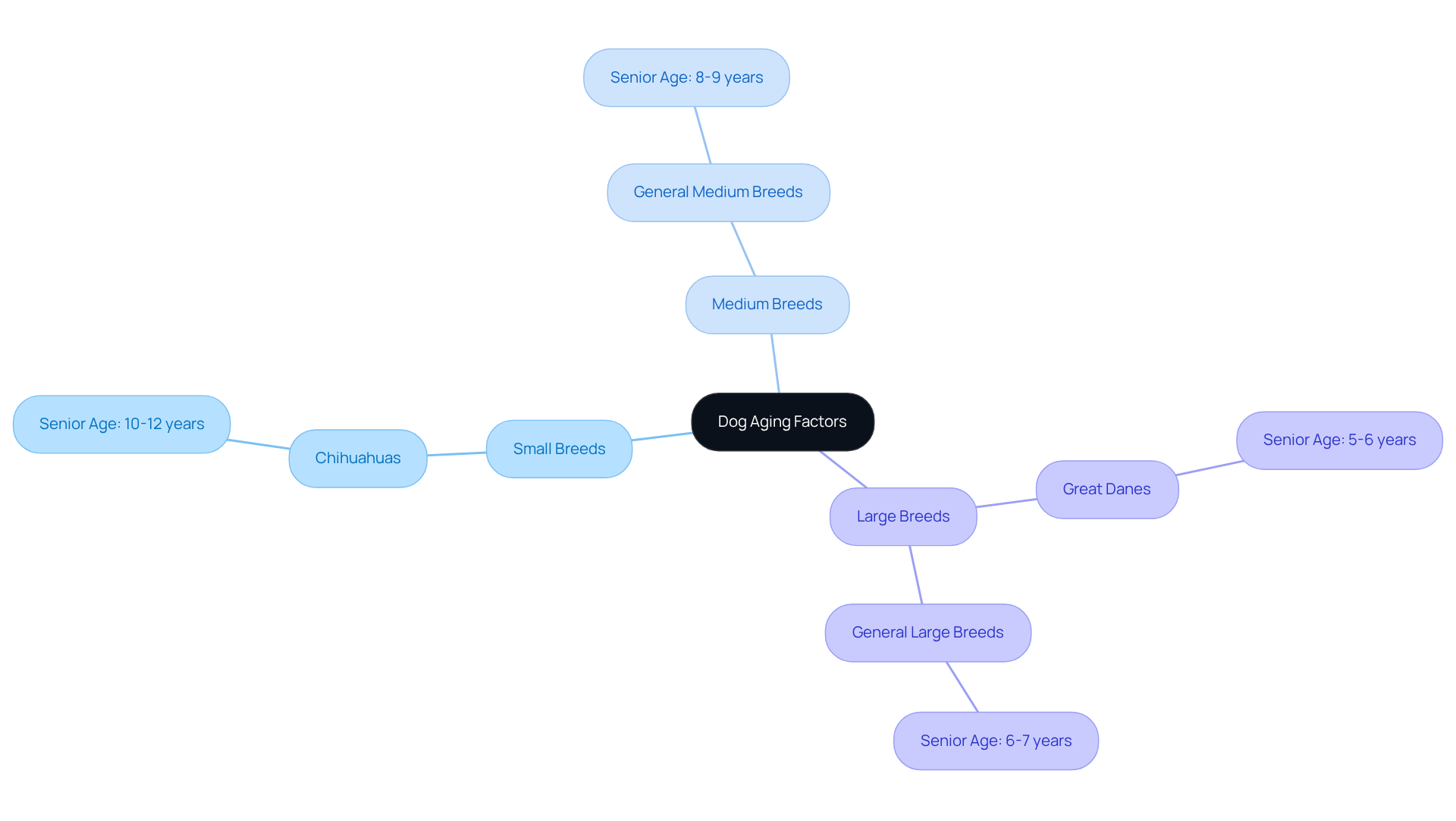
- Small breeds like Chihuahuas are typically considered seniors around 10-12 years of age.
- Larger breeds such as Great Danes may reach senior status as early as 5-6 years.
- Medium-sized dogs are generally seen as seniors at about 8-9 years.
The early stages of a dog’s life are particularly crucial, with the first stage equating to roughly 15 dog to human years, followed by an additional 9 years in the next stage. After this rapid aging period, the pace of aging slows down significantly, and the differences among breeds become more pronounced.
- Medium-sized breeds may be classified as seniors around 8-9 years.
- Large breeds often reach this milestone by 6-7 years.
As Randa Kriss wisely notes, “Every dog ages differently, just like humans.” Understanding these variations is vital for pet owners, as it enables them to tailor care and anticipate the evolving needs of their pets as they age. It’s also important to consult a veterinarian about modifying a senior dog’s diet and exercise to help maintain their health and happiness.
Utilize Scientific Insights: Modern Approaches to Accurately Calculate Dog Ages
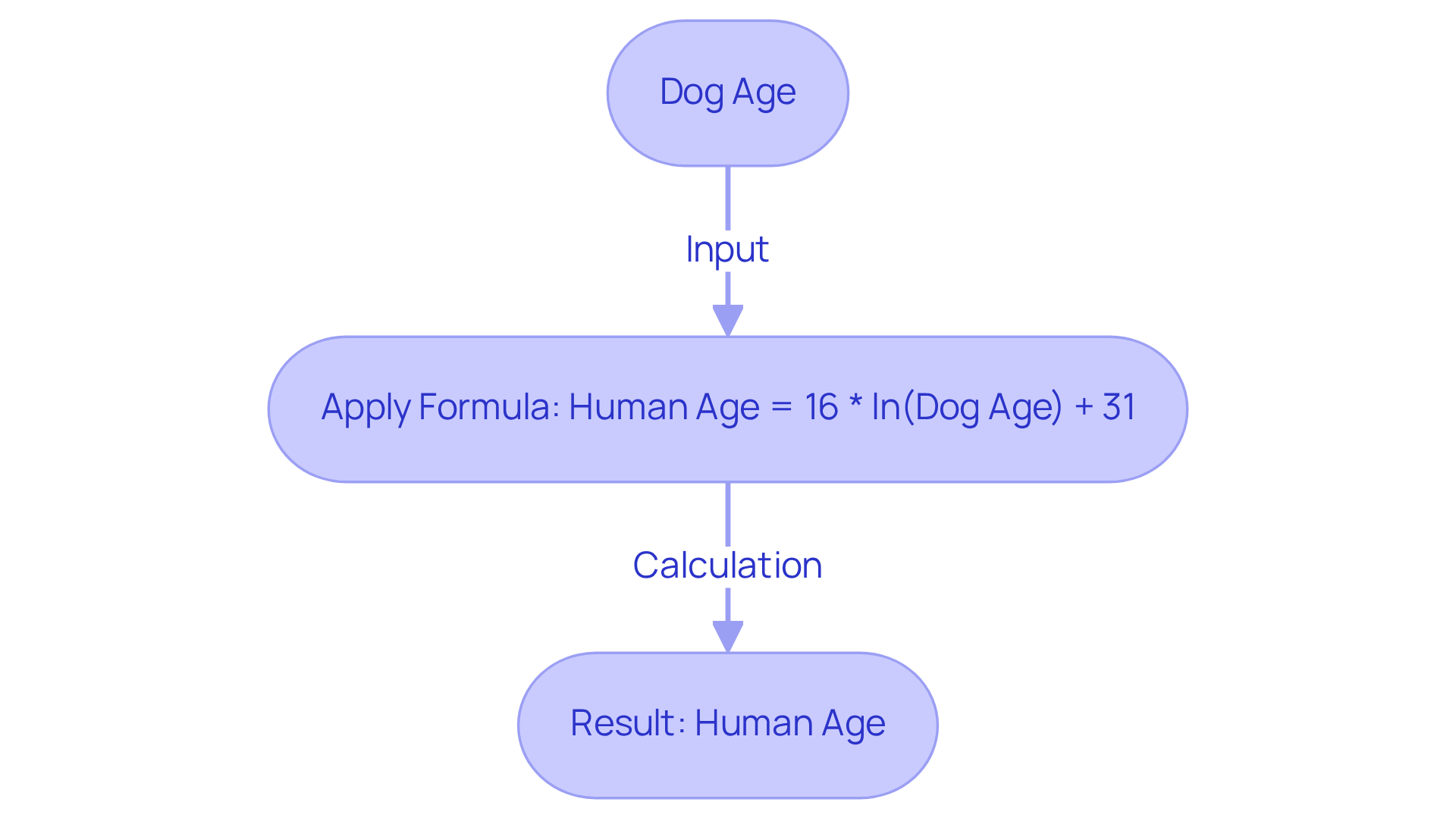
Recent research has transformed how we understand our beloved dogs’ aging process, moving beyond traditional formulas that might not fully capture their unique journeys. It’s heartening to know that a notable advancement involves the use of the natural logarithm of a dog’s age, offering a more accurate reflection of how they age. The formula:
Human Age = 16 * ln(Dog Age) + 31
is based on extensive studies, including one that thoughtfully analyzed blood samples from 105 Labrador retrievers. This approach recognizes the biological changes that occur as dogs grow older, taking into account factors such as breed size and genetic predispositions. This tailored understanding of a dog’s age is crucial, especially since canine aging slows down significantly by the age of seven, highlighting the importance of precise evaluations.
Moreover, many online calculators and tools now embrace this formula, making it easier for pet owners to convert their dog’s age to human years. As Randa Kriss insightfully notes, “In truth, canines age more quickly than people in their initial stages, but their aging process decelerates in subsequent stages.” By adopting these modern methodologies, pet owners can ensure they are providing age-appropriate care, nutrition, and exercise that cater to their dog’s unique needs, ultimately enhancing their overall well-being. The outdated 7:1 ratio for dog to human years is no longer deemed accurate, further reinforcing the necessity for these new approaches.
In recognizing these advancements, we can better connect with our furry companions and ensure they receive the love and care they truly deserve.
Apply Knowledge: The Importance of Understanding Your Dog’s Age for Health and Care
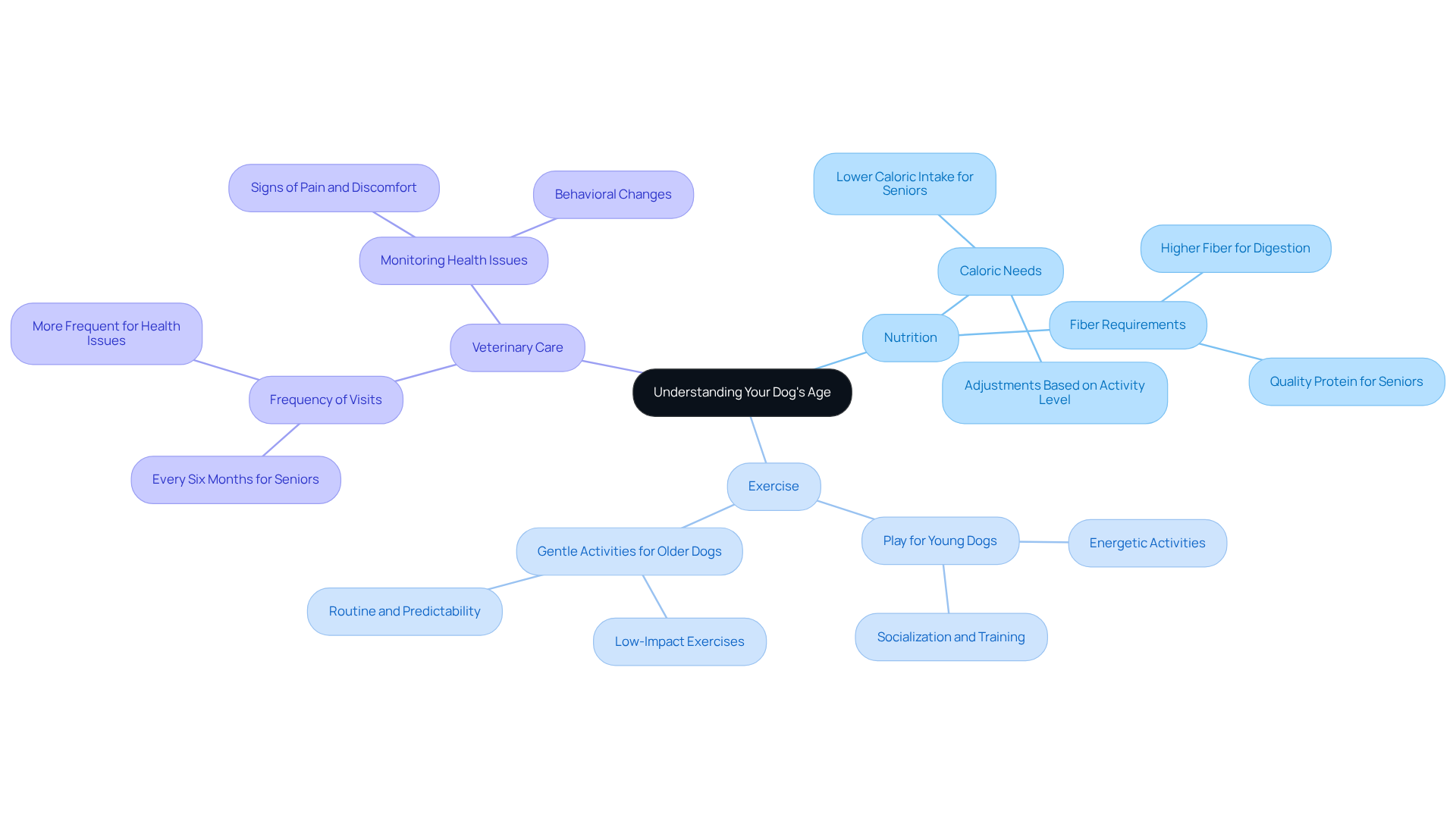
Understanding your dog’s age in dog to human years is crucial for ensuring their health and well-being. As pet owners, we often worry about providing the best care for our furry companions, and recognizing how age influences their dietary needs is a significant part of that. Older dogs typically require a different nutritional profile than younger ones, often benefiting from diets that are lower in calories yet higher in fiber. This adjustment aids in weight management and supports digestion. It’s generally recommended that dogs transition to senior pet food around age 6, which is equivalent to about 40 to 42 in dog to human years, depending on their size, to meet their evolving nutritional requirements.
Age also plays a vital role in determining exercise needs. While puppies and young dogs thrive on energetic play, older dogs need gentler, low-impact activities to maintain their mobility without the risk of overexertion. Regular, age-appropriate exercise is essential not only for preventing obesity but also for promoting joint health, especially since many older dogs may face conditions like arthritis. Maintaining a lean body condition throughout their lives can even extend a dog’s median lifespan by 15% in terms of dog to human years—a comforting thought for any pet owner.
Moreover, being mindful of your dog’s age is essential for scheduling veterinary check-ups and vaccinations. Older dogs often require more frequent visits to monitor age-related health issues, such as dental concerns and organ function. It’s advisable to schedule regular wellness visits at least every six months to catch potential health problems early. Additionally, it’s important to watch for signs of pain, such as limping or whining, and to ensure they have ample access to fresh, clean water to prevent dehydration. By being aware of these aspects, you can provide your furry friend with the optimal care they deserve, tailored to their life stage.
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of converting dog years to human years is essential for pet owners who wish to provide the best care for their furry companions. The outdated belief that one dog year equals seven human years oversimplifies the unique aging process of dogs, which varies significantly based on breed, size, and overall health. By employing a more accurate formula that reflects the biological changes dogs undergo, pet owners can gain invaluable insights into their pets’ life stages and health requirements.
Throughout this discussion, we recognize the emotional weight that comes with caring for our beloved pets. The significant differences in aging rates among various breeds remind us that each dog is unique, necessitating tailored nutrition and exercise as they age. Regular veterinary check-ups play a vital role in monitoring health changes, ensuring that our companions receive the best possible care. Understanding these factors not only enhances the quality of life for dogs but also strengthens the bond between pets and their owners, allowing for more informed decisions regarding care.
Ultimately, acknowledging the scientific advancements in understanding dog aging encourages a more compassionate approach to pet ownership. By staying informed and adapting care to fit the specific needs of dogs at different life stages, we can ensure our beloved companions enjoy healthier, happier lives. Embracing this knowledge is a powerful step toward fostering a deeper connection with our pets and providing them with the love and care they truly deserve.
